UK Energy Price Cap Explained (Properly)

If you’ve ever been baffled by the UK energy price cap, you’re not alone. Let’s break it down simply.
What is the UK Energy Price Cap?
The energy price cap is a limit set by Ofgem (the energy regulator) on the maximum amount energy suppliers can charge per unit of gas and electricity. It also caps daily standing charges (the fixed amount you pay to have access to energy). It is NOT a cap on your total bill—what you pay depends on how much energy you use.
Why Does the UK Energy Price Cap Exist?
It was introduced to stop energy companies from overcharging customers on default (standard variable) tariffs. Instead of letting prices skyrocket unchecked, Ofgem reviews the cap every three months to reflect market conditions.
Why Is the UK Energy Price Cap Confusing?
A common misconception is that the price cap limits your total bill. In reality, it only sets maximum rates for unit prices (per kWh) and standing charges. The “total bill” figures you often see in headlines assume a typical household’s usage, but your actual bill depends entirely on how much energy you consume.
Ofgem often makes annoucements like this, which are entirely unhelpful to 99.9% of people:
From today, 1 October 2024, the energy price cap for a typical household that uses gas and electricity and pays by Direct Debit will go up from £1,568 to £1,717 per year. This is an increase of around 10% which adds around £12 a month to an average bill.
Who is this “typical household”? And how much energy do they consume? What type of house do they live in? And how is it heated and powered and insulated? Without knowing any of this it is impossible to tell how the yearly payment figures relate to our own situations.
Building on Ofgems unhelpful annoucements the media often picks up these figures and presents them as if they apply to everyone, which leads to even more confusion. But the truth is your bill will always be based on your own energy usage, not a fixed total.
UK Energy Price Cap Rates
The UK energy price cap changes based on wholesale energy costs and should really have been communicated using pence per kilowatt hour figures from the outset, as in the table below, which shows how the rate have changed over time:
| Period | Electricity (per kWh) | Gas (per kWh) | Standing Charge (Electricity) | Standing Charge (Gas) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July – September 2023 | 30.1p | 7.5p | 53.0p/day | 29.1p/day |
| October – December 2023 | 27.4p | 6.89p | 53.4p/day | 29.6p/day |
| January – March 2024 | 28.6p | 7.42p | 53.4p/day | 29.6p/day |
| April – June 2024 | 24.5p | 6.04p | 60.1p/day | 31.4p/day |
| July – September 2024 | 22.4p | 5.48p | 60.1p/day | 31.4p/day |
| October – December 2024 | 24.5p | 6.24p | 60.1p/day | 31.66p/day |
| January – March 2025 | 24.86p | 6.34p | 60.97p/day | 31.65p/day |
| April – June 2025 | 27.03p | 6.99p | 53.80p/day | 32.67p/day |
The rates represent the maximum you can be charged, so your bill depends on your actual energy consumption, but your supplier cannot charge more than the capped rates.
How to Save Money on Your Electricity Bill
Now that we know how the price cap works, how can households actually cut costs?
1. Consider Fixed Energy Deals – Are They Worth It?
- Fixed tariffs lock in a unit price for a set period, shielding you from price hikes.
- They can be cheaper than the price cap, but only if wholesale prices are stable or falling.
- Right now, many fixed deals are hovering around the cap level, so always compare before committing.
- Check what you could save via Switchcraft, one of the simplest comparison tools.
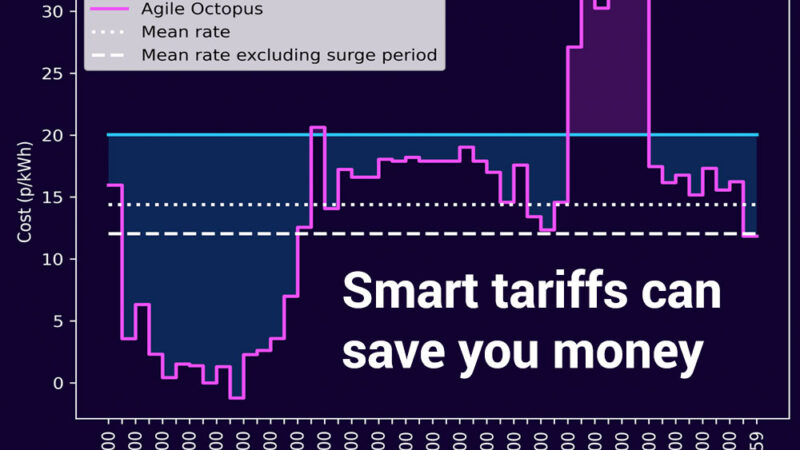
2. Is Octopus Agile a Smart Choice?
- Octopus Agile is a dynamic tariff where electricity prices change hourly based on wholesale costs.
- If you can shift your energy use to off-peak times (e.g., charging an EV or running appliances at night), it can save you a lot of money.
- However, if prices spike and you use energy during periods of high demand, your bill could rise, so it’s best for people who can be flexible with their energy use.
- Read more about how smart tarrifs can save you money and explore Octopus Agile.
3. Simple Ways to Cut Energy Costs
We’ve published our Top 10 energy saving tips, which provide full details of ways to cut costs, but some key steps to take include:
- Improving home efficiency: Smart thermostats, LED bulbs, and proper insulation can make a big difference.
- Using appliances wisely: Wash clothes at lower temperatures, avoid standby mode, and air-dry instead of using a tumble dryer.
- Monitoring your usage: A smart meter helps track what you’re spending in real time.
Bottom Line
The energy price cap offers some protection, but it won’t always mean the cheapest bills. If you’re looking to save, compare fixed deals, consider smart tariffs like Octopus Agile, and be mindful of your energy use. Small changes can lead to big savings!